Buy Air Asia merchandise online
 AirAsia, the leading and largest low-cost carrier in Asia, services the most extensive network with 122 routes covering more than 65 destinations. Within the grasp of 7 years of operation, AirAsia has carried over 65 million passengers and grown its fleet from just two aircraft to 80. The airline today is proud to be a truly Asean (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) airline with established operations based in Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand, servicing a network stretching across all Asean countries, China, India and Bangladesh. This is further complemented by AirAsia X, its low cost long-haul affiliate carrier that currently flies to destinations in China, Australia and the UK. AirAsia is the only regional carrier with the largest destination network and highest flight frequencies. AirAsia has been awarded the 2009 World’s Best Low Cost Airline in the annual World Airline Survey by Skytrax.
AirAsia, the leading and largest low-cost carrier in Asia, services the most extensive network with 122 routes covering more than 65 destinations. Within the grasp of 7 years of operation, AirAsia has carried over 65 million passengers and grown its fleet from just two aircraft to 80. The airline today is proud to be a truly Asean (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) airline with established operations based in Malaysia, Indonesia and Thailand, servicing a network stretching across all Asean countries, China, India and Bangladesh. This is further complemented by AirAsia X, its low cost long-haul affiliate carrier that currently flies to destinations in China, Australia and the UK. AirAsia is the only regional carrier with the largest destination network and highest flight frequencies. AirAsia has been awarded the 2009 World’s Best Low Cost Airline in the annual World Airline Survey by Skytrax.

Monday, June 29, 2009 | Labels: AirAsia | 3 Comments
The application of 3rd party certification programme in Malaysia
In today's world, electronic commerce is a fast growing industry. Businessmen are transferring their businesses onto the Web in order to increase the sales of their goods and services beyond their geographical area. This helps them to use better options for selling and buying. They also have the option to sell their products directly without the help of distributors or middlemen.
When it comes time to enter personal information or complete a business transaction on the Internet, most people hesitate, and understandably so. They've read about credit card fraud, identity theft, spoofing, hacking, phishing and other abuses. It should come as no surprise that many e-shoppers are still concerned about security and privacy issues. As such, you've got to convince them that you are trustworthy in three specific areas: security, privacy and reliability.
In fact, the sole goal of digital certificates is to make sure online shoppers feel secure, by authenticating the legitimacy of the certificate owner and by protecting your sensitive data.
Digital certificates are issued by a third-party certificate authority. The certificate authority will only issue a digital certificate after they have thoroughly checked out a company.
 Digicert Sdn Bhd is the first certification authority in Malaysia licensed to issue digital signature and digital certificate. DIGICERT is a smart partnership between POS Malaysia Berhad and MIMOS Berhad. They are the leading Certification Authority (CA) in Malaysia providing trust solutions fore-businesses. It provides a safe environment for business-to-business transactions, a sure route to reduce costs and gain efficiency. It allows consumers that trade through the Internet to sign electronically - in the form of adigital signature that is in line with the requirements of the Malaysian Digital Signature Act 1997 and the Digital Signature Regulations 1998. Its trust solutions are legally recognized under Malaysian law.
Digicert Sdn Bhd is the first certification authority in Malaysia licensed to issue digital signature and digital certificate. DIGICERT is a smart partnership between POS Malaysia Berhad and MIMOS Berhad. They are the leading Certification Authority (CA) in Malaysia providing trust solutions fore-businesses. It provides a safe environment for business-to-business transactions, a sure route to reduce costs and gain efficiency. It allows consumers that trade through the Internet to sign electronically - in the form of adigital signature that is in line with the requirements of the Malaysian Digital Signature Act 1997 and the Digital Signature Regulations 1998. Its trust solutions are legally recognized under Malaysian law.
DIGICERT is proud to be the Certification Authority in many strategic projects, to name a few eGovernment, ePerolehan, Online Pharmaceutical, MyKad PKI and PKI-based Internet Banking. The launching of e-Filing Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN) project in which DIGICERT was chosen to be the premier CA, marked another milestone to the healthy growth of secured e-commerce and transactions using a digital certificate over the Internet in Malaysia. Their projects are from various sectors of the economy, including manufacturing, education, technology, emerging business, professional services, healthcare, telecommunications, financial, architecture and insurance sectors.
DIGICERT provides certification management services as follows:
* Screening of the authority of the people that apply for issuance and revocation of certificates.
* Issuance, revocation and publication of certificates.
* Delivery, storage and archiving of certificates and certificates revocation list.
The end-user product of the service is a digital certificate. A digital certificate is used by an entity as a credential to provide virtual identity or other security-related functions. The entity that possesses the certificate is known as a Subscriber. A Subscriber can be an individual, an organization, a device or an individual. The credential is then used, for example, to access a website or service of a business. An organization that relies on the digital certificate as a form of identity is known as a "Relying Party." DIGICERT uses PKI-based Identity Management that has distinct entities with defined areas of responsibilities. These entities include Certification Authority (CA), Subscribers, and Relying Parties (RP). Each entity has specific roles, with associated obligations, and may have direct contractual relationships with one another or be non-affiliated. Digital certificate is stored on smartcard e.g. MyKad, USB token, floppy disk and computer hard disk.
 Msctrustage.com is the second certification authority company in Malaysia to provide security services such as issuing digital certificates, establishing public key infrastructureand providing cryptographic technology to various Internet markets. Since its formation, MSC Trustgate.com Sdn Bhd, as the Malaysia's premier licensed Certification Authority and an affiliate of VeriSign Inc., an international Internet security company, has diligently geared itself to become a disciplined, market-leader and strategic provider of cutting-edge security infrastructure solutions. Today, MSC Trustgate.com is the leading provider of Internet trust and security solutions in ASEAN. Over 500 companies across industry rely on our solution for secure e-business and e-commerce.
Msctrustage.com is the second certification authority company in Malaysia to provide security services such as issuing digital certificates, establishing public key infrastructureand providing cryptographic technology to various Internet markets. Since its formation, MSC Trustgate.com Sdn Bhd, as the Malaysia's premier licensed Certification Authority and an affiliate of VeriSign Inc., an international Internet security company, has diligently geared itself to become a disciplined, market-leader and strategic provider of cutting-edge security infrastructure solutions. Today, MSC Trustgate.com is the leading provider of Internet trust and security solutions in ASEAN. Over 500 companies across industry rely on our solution for secure e-business and e-commerce.
Related Links:
Sunday, June 28, 2009 | Labels: 3rd party certification, Digicert Sdn Bhd, Msctrustage.com | 3 Comments
How to safeguard our personal and financial data?
Nowadays, internet is one of the ways that connect billions of computers throughout the world. People rely mostly on the computer especially the internet to store and manage their so called personal and financial information. Information travels rapidly through the internet. Information becomes vulnerable and easily expose to threat when they are travelled via the internet. That is why internet security is very important for most of the internet user.
There are few ways which users are able to safeguard their personal and also financial data:
(a) Install a firewall
A firewall is a software program designed to allow good people in and keep bad people out. Nowadays, most of the computers come with firewalls integrated into their operating systems. Users who use DSL or cable modem have an added layer of protection because these modems come with another firewall built in.
(b) Install and update antispyware and antivirus programs
Microsoft and numerous application vendors offer users regular updates to existing antispyware programs, so be on the lookout. As for antivirus protection, Symantec and Norton antivirus are popular choices.
(c) Avoid accessing financial information in public
It is best for the user not to check their bank balance when working from a coffee shop such as starbucks, coffee bean that offers free wireless access. Although the system are convenient to access but it is unknown. Casual users have no way of assessing how sturdy their firewalls are.
(d) Update your browser
User is encouraged to update theirs browser on a regular basis. This is can help plug up security holes, so as to make it a habit.
(e) Look for "locks"
How can you tell if your financial site is really secure before you log on? The Web address should start with "https" instead of "http" says Weston. Also, look for small lock icon in the lower-right corner of the browser window.

(f) Don't open mystery attachments
It is very important to never open an attachment or click on a link sent to user by an unknown party. The attachments can contain viruses and links can lead unsuspecting users to dummy sites where they are asked to input financial information.
(g) Use a credit card with a small limit
User is encouraged to use a credit card with a small limit for mail-order and online purchases. It is very easy for a dishonest sales clerk to use user’s credit card information. If the card user use for these purchases has a low credit limit, at least thieves won't be able to rack up many bills before hitting a wall.

(h) Choose your PIN wisely
When user wants to choose something that he or she could easily remember, the pin should not be something that a clever thief could figure out just by learning your birth date or your child's name. A combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols will offer user more security.
(i) Pay attention when using an ATM
User must keep his or her eyes peeled for anyone who seems a little too interested in the transactions. Use a free hand to shield the keypad when entering the PIN. Besides that, banker can add on fingerprint scanning on ATM machine.
Related Links:
1. http://finance.yahoo.com/banking-budgeting/article/103893/Six-Ways-to-Safeguard-Your-Online-Assets
2. http://abcnews.go.com/Technology/wireStory?id=5351346
3. http://www.fool.com/personal-finance/general/2006/09/23/safeguard-your-financial-life.aspx
4. http://amazingcommerce.wordpress.com/2008/06/18/how-to-safeguard-our-personal-and-financial-data/
Sunday, June 28, 2009 | Labels: Safeguard financial data, Safeguard personal data | 1 Comments
Phishing: Examples and its prevention methods
The term phishing comes from the fact that Internet scammers are using increasingly sophisticated lures as they "fish" for users' financial information and password data.
In the field of computer security, phishing is the criminally fraudulent process of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Communications purporting to be from popular social web sites, auction sites, online payment processors or IT Administrators are commonly used to lure the unsuspecting public.
Phishing is typically carried out by e-mail or instant messaging, and it often directs users to enter details at a fake website whose look and feel are almost identical to the legitimate one. (This is why phishing is also called brand spoofing). Even when using server authentication, it may require tremendous skill to detect that the website is fake. Phishing is an example of social engineering techniques used to fool users, and exploits the poor usability of current web security technologies. Attempts to deal with the growing number of reported phishing incidents include legislation, user training, public awareness, and technical security measures.
A phishing technique was described in detail in 1987, and the first recorded use of the term "phishing" was made in 1996. The term is a variant of fishing, probably influenced by phreaking, and alludes to baits used to "catch" financial information and passwords.
Free Money in Three Easy Steps
The first step is to reach as many possible potential victims in the shortest amount of time with the least amount of effort. The below is a typical e-mail call to action as rendered by Microsoft’s Outlook Express.
In later sections, the structure of various tactics of phishers will be explored. Generally speaking, most phishing e-mail will appear similar in both appearance and structure. Virtually all will have one common feature: a clickable link to a fake site that has been built to look similar or identical to the legitimate site it's masquerading as.
The Catch:
A fraction of the potential victim pool, sometimes as much as two to three percent, fulfill the following criteria:
• They are customers of the phisher’s chosen brand (Citibank, PayPal, etc.).
• They become sufficiently convinced the message (and supplied link) is a valid communication from their financial institution.
• Their immediate action is required to prevent a catastrophe (or, rarely, collect a reward).Once these requirements are met, the attacker must also provide these qualified victims with a credible facsimile of the targeted brand’s login page, such as the (fake) site below:
Often, these forms lead to a second page, which collects even more account-relevant information, specifically, account numbers and PINs.
However, even if a user provided an accurate password, that could change before the phisher has a chance to log in to the newly acquired victim account. So once account information has been collected, the most straightforward next step would be to log in to the phished account and perform an electronic funds transfer.
Examples of phishing:
Phishers typically include upsetting or exciting (but false) statements in the emails to get people to react immediately. They will ask for information such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, social security numbers, date of birth, etc. PayPal showed above is only one of the examples of phishing email. Besides that, there are First Generic Bank, Citibank, Bank of America, Bank of Scotland, HSBC, ebay, Intelligent Finance, Nationwide and so on. The phishing threat is spread all over the world through internet.




Prevention methods
In order to prevent becoming the victim of phishing, users must always alert of the emails received. There are tips on how to avoid the Internet scam:
- Be suspicious of any email with urgent requests for personal financial information unless the email is digitally signed.
- If you receive an unexpected e-mail saying your account will be shut down unless you confirm your billing information, do not reply or click any links in the e-mail body. Instead, call the company on the telephone, or log onto the website directly by typing in the Web address in your browser.
- Avoid filling out forms in email messages that ask for personal financial information. You should only communicate information such as credit card numbers or account information via a secure website or the telephone.
- Before submitting financial information through a Web site, look for the "lock" icon on the browser's status bar. It means your information is secure during transmission.
- If you are uncertain about the information, contact the company through an address or telephone number you know to be genuine.
- Consider installing a Web browser tool bar to help protect you from known fraudulent websites. These toolbars match where you are going with lists of known phisher Web sites and will alert you.
- Regularly log into and check your online accounts, bank, credit and debit card statements to ensure that all transactions are legitimate. Don't leave it for as long as a month before you check each account. If anything is suspicious or you don't recognize the transaction, contact your bank and all card issuers.
- If you unknowingly supplied personal or financial information, contact your bank and Credit Card Company immediately.
- Use anti-virus and anti-spyware software, as well as a firewall, and update them all regularly. And always be cautious about opening any attachment or downloading any files from emails you receive, regardless of who sent them.
- Forward phishing emails to spam@uce.gov – and to the company, bank, or organization impersonated in the phishing email. You also may report phishing email to reportphishing@antiphishing.org. Suspicious e-mail can be forwarded to uce@ftc.gov, and complaints should be filed with the state attorney general's office or through the FTC at http://www.ftc.gov/. The Anti-Phishing Working Group, a consortium of ISPs, security vendors, financial institutions and law enforcement agencies, uses these reports to fight phishing.
Besides that, users can install Phishing Filter. It offers dynamic new technology to help protect internet users from Web fraud and the risks of personal data theft. Scams known as "phishing scams” typically attempt to lure users into visiting phony Web sites where the personal information or credit card information can be collected for criminal use. This form of identity theft is growing quickly on the Web.
Phishing Filter includes several patent-pending technologies designed to warn or block users from potentially harmful Web sites. There are three ways Phishing Filter helps to protect:
1. A built-in filter in your browser that scans the Web addresses and Web pages you visit for characteristics associated with known online Web fraud or phishing scams, and warns you if sites you visit are suspicious.
2. An online service to help block you from confirmed scams with up-to-the-hour information about reported phishing Web sites. (Phishing sites often appear and disappear in 24–48 hours, so up-to-the-hour information is critical to protection.)
3. A built-in way for you to report suspicious sites or scams. With Phishing Filter, you can help provide valuable information on any Web sites you believe are potentially fraudulent phishing attacks. You submit the information to Microsoft and Microsoft evaluates it. If the information is confirmed, the online service adds the information to a database to help protect the community of Internet Explorer users.
Related Links:
1. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phishing
2. http://www.wordspy.com/words/phishing.asp
3. http://www.planb-security.net/wp/503167-001_PhishingDetectionandPrevention.pdf
4. http://www.phishtank.com/what_is_phishing.php?view=website
5. http://www.flickr.com/photos/brennansg/290704431/sizes/o/
6. http://www.flickr.com/photos/23385905@N04/3333805334/
7. http://www.antiphishing.org/consumer_recs.html
8. http://www.onguardonline.gov/topics/phishing.aspx
9. http://www.microsoft.com/protect/products/yourself/phishingfilter.mspx
Saturday, June 27, 2009 | Labels: Example of phishing, Phishing, Phishing prevention methods | 1 Comments
The threat of online security: How safe is our data?
Just about anyone that gets online is at risk. Online security threats are one of the biggest challenges on the Internet today. The problem is that the people that want to attack your computer and the computers of the people that you know don't create difficult methods to create problems instead they focus on common failures that will give them access. When those that get on the Internet know how these attacks take place, these attacks can be lessened and even prevented in most cases.
The best thing you can do if you get on the Internet at all is to use security software and hardware such as firewalls and authentication servers, as this is the most effective way to protect your computer and your personal information.
 1. Computer viruses
1. Computer virusesThe most common form of malicious code is a computer virus, a program or a fragment of code that replicates by attaching copies of itself to other programs.
There are four main classes of viruses:
(a) The first class consists of file infectors, which imbed themselves into ordinary executable files and attach to other system executables when the file is run.
(b) The second category is system or boot-record infectors, which infect the first sector on a driver from which the operating system is booted-up. These viruses are not as prevalent now that floppy disks are less frequently used.
(c) The third group of viruses is called macro viruses, which infect data files that include scripting "macros."
(d) Finally, viruses that use more than one attack method are called multi-part viruses.
 For example, the May 2000 "I LOVE YOU" virus was even simpler a small piece of code attached to electronic mail. Double-clicking on the executable caused it to send an e-mail to everyone in an address book, subsequently damaging victims' machines. Fast-spreading viruses like "I LOVE YOU" cause e-mail servers to overload and businesses to shut down email correspondence. For example, in one day, the "I LOVE YOU" virus caused over $100 million in United States damages and over $1 billion in worldwide losses.
For example, the May 2000 "I LOVE YOU" virus was even simpler a small piece of code attached to electronic mail. Double-clicking on the executable caused it to send an e-mail to everyone in an address book, subsequently damaging victims' machines. Fast-spreading viruses like "I LOVE YOU" cause e-mail servers to overload and businesses to shut down email correspondence. For example, in one day, the "I LOVE YOU" virus caused over $100 million in United States damages and over $1 billion in worldwide losses. 2. Denial of Service Attacks (DOS)
2. Denial of Service Attacks (DOS) DOS is another form of malicious code, are carefully crafted and executed. DOS attacks are not new, yet they are growing in sophistication. Traditional DOS attacks usually involve one computer attacking another, but the use of multiple computers in a highly organized attack is becoming increasingly common. Such attacks, known as Distributed Denial of Service attacks (DDOS), were witnessed in a number of large corporate computer shutdowns in 2000. Understanding the technical components of a DDOS attack is important, since these attacks precisely reveal the vulnerabilities inherent to the Internet. A DDOS attack functions by overwhelming a server with a deluge of messages that appear to be normal.
It is a broad term covering Internet transactions that involve falsified information. Some of the most common forms of online fraud are the sale via Internet of counterfeit documents, such as fake IDs, diplomas, and recommendation letters sold as credentials; offers of easy money, such as work at-home offers that claim to earn individuals thousands of dollars for trivial tasks; prank calls, in which dial-up connections lead to expensive long distance charges; and charity facades, where donations are solicited for phony causes.
 4. Phishing
4. PhishingIt is a technique used to gain personal information for purposes of identity theft, using fraudulent e-mail messages that appear to come from legitimate businesses. These authentic-looking messages are designed to fool recipients into divulging personal data such as account numbers and passwords, credit card numbers.
 5. Worms
5. WormsA computer worm is a self-replicating computer program. It uses a network to send copies of itself to other nodes (computers on the network) and it may do so without any user intervention. A worm is similar to a virus by design and is considered to be a sub-class of a virus. Worms spread from computer to computer, but unlike a virus, it has the capability to travel without any human action. A worm takes advantage of file or information transport features on your system, which is what allows it to travel unaided. One example would be for a worm to send a copy of itself to everyone listed in your e-mail address book. Then, the worm replicates and sends itself out to everyone listed in each of the receiver's address book, and the manifest continues on down the line.
 6. Trojan horse
6. Trojan horseThe Trojan Horse, at first glance will appear to be useful software but will actually do damage once installed or run on your computer. Those on the receiving end of a Trojan Horse are usually tricked into opening them because they appear to be receiving legitimate software or files from a legitimate source. When a Trojan is activated on your computer, the results can vary. Some Trojans are designed to be more annoying than malicious (like changing your desktop, adding silly active desktop icons) or they can cause serious damage by deleting files and destroying information on your system. Trojans are also known to create a backdoor on your computer that gives malicious users access to your system, possibly allowing confidential or personal information to be compromised. Unlike viruses and worms, Trojans do not reproduce by infecting other files nor do they self-replicate.
7. Web servers and services
Many default HTTP web servers expose visitors every time they log on to these websites. You should be sure that you have the patches available that have been released over the last few years and that your computer isn't utilizing a default configuration.
 8. Spyware attacks
8. Spyware attacksSpyware attacks are something that we are probably all familiar with, as they are the most common online security threat faced by Internet users. Spyware is simply a computer program that is designed to steal information from your computer without your knowledge. The software will typically be installed on your computer without you even knowing it, and then it will send your personal information such as documents, passwords, credit card numbers, bank accounts, and many others to another source. Common spyware includes Trojan horses, key loggers, dialers, and adware programs.
Online threats are very real, but if you know how you become vulnerable, you will be able to better protect yourself. You should be able to get online without constantly worrying.
1. Encrypt it
It's one of the most overlooked-and easily fixable-precautions that a small business can take.
2. Back it up
When data goes missing, it is often the only copy. Not only has the information potentially fallen into the wrong hands, but it's probably also lost forever. Make sure to back up all important files onto the company servers before leaving town. If those servers are in turn backed up to an e-vaulting provider, it may be possible to restore your files directly from the provider to your hastily-purchased replacement."
3. Travel smart with your technology
A few simple precautions can prevent data loss, that is never leave your laptop unattended. Don't leave it in the car, in the conference room, or in the workspace you're using at a client's office unless it is locked.
4. Do not work from an unsecured computer
Many hotels and conference centers offer courtesy PCs to guests so they can access e-mail while they're away. The single most important tip for securing road warrior information is to minimize work done on a local computer. The better way will be directly connect to a remote server for document and data management, preferable from your own PC or PDA. Many of these public computers are infected with spyware that monitors and records your keystrokes. It is important to not be lulled into a false sense of security.
5. Use a password
Believe it or not, many mobile devices lack even the most basic password-protection. Passwords are among the simplest and most reliable form of data protection available. There are four basic password rules. First, make sure your password is at least eight characters. Second, include at least one number, one capital letter and one special character, such as "#" (but don't use numbers instead of letters, such as m0us3, since password crackers check for these). Third, never use a word that can be found in a dictionary, thereby preventing a "dictionary attack." And finally, resist the urge to use personal information such as your birthday because this information can be found out.
6. Get on a stick
Instead of carrying your company's sensitive data on a PC or PDA, keep it on a memory stick or portable hard drive. It doesn't matter if your laptop is stolen or damaged, your data will be fine as long as you have the USB memory device. As a bonus, many of these devices allow you to encrypt the information on them, so even if they are lost, they're useless.
Having an ironclad policy about how to treat company laptops will take you a long way in keeping your data safe. Such a policy should be comprehensive. It should address what to do with a laptop, anytime and anywhere, regardless if the laptop is on, off or even online. A server that is deployed on the enterprise premise should terminate secure tunnels and manage user credentials, patch management and security policies.
There is a lot of bad stuff out there. Make sure your employees' mobile computing devices are protected. Be sure your laptop is equipped with the right blend of IT security: anti-spam, anti-spyware, a Virtual Private Network and a personal firewall because hackers use a variety of tactics to defeat security.
9. Educate your employees
If your people do not know what is out there, how can they take the necessary precautions? Mobile users should be aware of every site they visit and every communication they open on their mobile devices. Unsolicited communications, no matter how inviting, can contain threats to the mobile device. People should only open communications from known sources and limit mobile Internet browsing to trusted sites.
10. Don't be stupid
People display highly sensitive data, like company secrets and even information that could facilitate identity thefts, on their laptops. They do not bother to install an inexpensive polarizing overlay that could avoid shoulder-surfing. In other words, if your case says "IBM" or "HP" or "DELL" or even a well-known manufacturer of computer bags, you have increased your radar profile for thieves. There are lots of less noticeable bags out there that can help you avoid being the next victim.
11. Consider data-level security precautions
These add yet another layer of security to your documents, protecting them from would-be thieves. There are cost-effective security solutions on the market that are easily integrated with Microsoft products like Exchange, SharePoint and the Office suite. They provide a simple way for small businesses to benefit from these solutions without radically changing existing IT policies and procedures."
12. Do not leave well enough alone
If you're really concerned with security, these precautions just represent a good start. Experts say you should always be working to improve your safeguards, even as the bad guys try to crack your defenses. You have to control who can access your data. For companies that are serious about security, a user ID and password are not good enough. There should be some form of two-factor authentication, like a Smart Card, USB token or SoftCerts. But do not rely solely on passwords. Keeping your data safe while you're out of the office is an ongoing challenge.
Besides that, another way for company to secure customer information is outsourcing security service. But company has to be careful not to outsource privacy completely, or to rely too much on the consultant to make important decisions. Turn to outside help for direction, but always remain of its own programme.
Company should also limit the connectivity for example, limit downloads. Do not simply download software that you have never heard of, instead stick with the names that you know. You should also take care to scan all files before they are downloaded.
The employees of the company use only authorized media for loading data and software.
On the other hand, enforce the mandatory access controls. The employees of the company should always remember to scan their computer with Anti-virus. Delete all the cookies in the computer to prevent track on the history or password and on the firewall to prevent hackers.
In conclusion, with a few precautions and by taking a long view on mobile security, you can make sure the company’s valuable information does not fall into the wrong hands.
Related Links:
Saturday, June 27, 2009 | Labels: Online security | 3 Comments
Advantages and disadvantages of E-Commerce
 E-Commerce is playing a very essential role in the online business world. Although it is one of the best and cheapest intermediate ways for reaching out to new customers in the online market, but, if e-commerce implemented effectively, it also offers a smart way of doing online business & expanding it more. Furthermore, e-commerce is planned and implemented to provide customer with a convenient, satisfying and protected shopping experience.
E-Commerce is playing a very essential role in the online business world. Although it is one of the best and cheapest intermediate ways for reaching out to new customers in the online market, but, if e-commerce implemented effectively, it also offers a smart way of doing online business & expanding it more. Furthermore, e-commerce is planned and implemented to provide customer with a convenient, satisfying and protected shopping experience.
Advantages
1. Being able to conduct business
E-commerce systems can operate throughout the day. The physical storefront does not need to be open in order for customers and suppliers to be doing business with the company electronically.
2. Access the global marketplace
The Internet spans the world, and it is possible to do business with any business or person who is connected to the Internet. Simple local businesses such as specialist record stores are able to market and sell their offerings internationally using e-commerce. This global opportunity is assisted by the fact that, unlike traditional communications methods, users are not charged according to the distance over which they are communicating.
3. Speed
Electronic communications allow messages to traverse the world almost instantaneously. There is no need to wait weeks for a catalogue to arrive by post: that communications delay is not a part of the Internet / e-commerce world.
4. Marketplace
The market in which web-based businesses operate is the global market. It may not be evident to them, but many businesses are already facing international competition from web-enabled businesses
5. Opportunity to reduce costs
The Internet makes it very easy to 'shop around' for products and services that may be cheaper or more effective than we might otherwise settle for. It is sometimes possible to, through some online research, identify original manufacturers for some goods - thereby bypassing wholesalers and achieving a cheaper price.
Disadvantages
1. Time for delivery of physical products
E-commerce is often used to buy goods that are not available locally from businesses all over the world, meaning that physical goods need to be delivered, which takes time and costs money.
2. Physical product, supplier & delivery uncertainty
In some aspects e-commerce purchases are made on trust. This is because, firstly, not having had physical access to the product, a purchase is made on an expectation of what that product is and its condition. Secondly, because supplying businesses can be conducted across the world, it can be uncertain whether or not they are legitimate businesses and are not just going to take your money. Thirdly, even if the item is sent, it is easy to start wondering whether or not it will ever arrive.
3. Returning goods
Returning goods online can be an area of difficulty. The uncertainties surrounding the initial payment and delivery of goods can be exacerbated in this process. Will the goods get back to their source? Who pays for the return postage? Will the refund be paid? Will I be left with nothing? How long will it take? Contrast this with the offline experience of returning goods to a shop.
4. Privacy, security, payment, identity, contract
Many issues arise - privacy of information, security of that information and payment details, whether or not payment details (e.g. credit card details) will be misused, identity theft, contract, and, whether we have one or not, what laws and legal jurisdiction apply.
Related Links:
1. http://www.smarte-commerce.com/advantages-of-e-commerce-in-present-business-scenario/
2. http://www.marcbowles.com/sample_courses/amc/ec1/ec1_3.htm
3. http://www.isos.com.my/ecommerce/advantages.htm
4. http://wiki.media-culture.org.au/index.php/E-commerce_-_Overview_-_Advantages
Monday, June 22, 2009 | Labels: Advantages of E-Commerce, Disadvantages of E-Commerce | 0 Comments
Revenue Model for Google, eBay & Amazon.com
E-Commerce Revenue Model describes how the publisher’s websites will earn revenue, generate profits, and produce a superior return on invested capital. The 5 major types are sales, transaction fees, subscription fees, advertising fees, affiliate fees.
Sales - Sales of goods, merchandise information and services provided in the publishers' websites.
Advertisement fees - Publishers can allocate some advertisements spaces in their website for other companies to place their banners or advertisement, in return for a fee named advertisement fees.
Subscription fees - customers would have to pay a fixed amount of fees either monthly or yearly when they are subscribing to contents and services offered by the website.
Affiliate fees - Companies receive commissions for referring customers to others' websites. It can include CPM (cost per thousand impressions), CPC (cost per click) and CPA (cost per acquisition/action).
 Google Inc. is an American public corporation, earning revenue from advertising related to its Internet search, e-mail, online-mapping, office productivity, social networking and video sharing services as well as selling advertising-free versions of the same technologies. 99% of Google's revenue is derived from its advertising programs. For the 2006 fiscal year, the company reported US$10.492 billion in total advertising revenues and only US$112 million in licensing and other revenues. Google offers targeted advertising solutions and global Internet search solutions. Its principal products and services include:
Google Inc. is an American public corporation, earning revenue from advertising related to its Internet search, e-mail, online-mapping, office productivity, social networking and video sharing services as well as selling advertising-free versions of the same technologies. 99% of Google's revenue is derived from its advertising programs. For the 2006 fiscal year, the company reported US$10.492 billion in total advertising revenues and only US$112 million in licensing and other revenues. Google offers targeted advertising solutions and global Internet search solutions. Its principal products and services include:
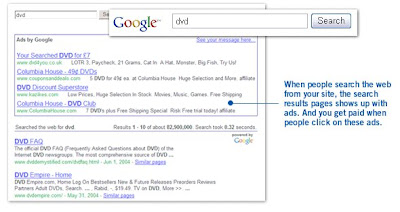
 Google AdSense. It is an ad serving program run by Google. It provides a fast and easy way for website publishers of all sizes to display relevant Google ads on their website's content pages and earn money. It's also a way for website publishers to provide Google web and site search to their visitors, and to earn money by displaying Google ads on the search results pages. Website owners can enroll in this program to enable text, image and, video advertisements on their sites. Revenue is generated through affiliate fees which on a per-click or per-thousand-ads-displayed basis and the ads are administered by Google. AdSense program includes AdSense for search and AdSense for content. AdSense for search was launched in the first quarter of 2002 and is Google’s service for distributing relevant ads from its advertisers for display with search results on the Google Network members’ sites. AdSense for content, launched in the first quarter of 2003, distributes ads from Google’s advertisers that are relevant to content on Google Network members’ sites. Google advertisers are required to pay Google a fee each time a user clicks on one of their ads displayed on Google Network members’ web sites.
Google AdSense. It is an ad serving program run by Google. It provides a fast and easy way for website publishers of all sizes to display relevant Google ads on their website's content pages and earn money. It's also a way for website publishers to provide Google web and site search to their visitors, and to earn money by displaying Google ads on the search results pages. Website owners can enroll in this program to enable text, image and, video advertisements on their sites. Revenue is generated through affiliate fees which on a per-click or per-thousand-ads-displayed basis and the ads are administered by Google. AdSense program includes AdSense for search and AdSense for content. AdSense for search was launched in the first quarter of 2002 and is Google’s service for distributing relevant ads from its advertisers for display with search results on the Google Network members’ sites. AdSense for content, launched in the first quarter of 2003, distributes ads from Google’s advertisers that are relevant to content on Google Network members’ sites. Google advertisers are required to pay Google a fee each time a user clicks on one of their ads displayed on Google Network members’ web sites. eBay Inc. is an American Internet company that manages eBay.com, an online auction and shopping website in which people and businesses buy and sell a broad variety of goods and services worldwide. eBay do not have inventory, it generates revenue from a number of fees. The eBay fee system is quite complex; there are fees to list a product (Insertion Fee) and fees when the product sells (Final Value Fee), plus several optional adornment fees, all based on various factors and scales. eBay may earned transaction fees from each successful transaction made by the bidders or sellers. eBay now owns the Paypal payment system which has fees of its own. Paypal founded in 1998 and acquired by eBay Inc. in October 2002. Paypal enables any individual or business with an email address to securely, easily and quickly send and receive payments online. Paypal's service builds on the existing financial infrastructure of bank accounts and credit cards and uses the world's most advanced proprietary fraud prevention systems to create a safe payment solution. A global leader in online payment solutions, Paypal has tens of millions of registered accounts and is accepted by millions of merchants worldwide, on and off eBay. Revenues from PayPal's transaction fees were $243.9 million, a gain of 51 percent from the year-ago quarter and 145 percent from querter2 2003. And the number of registered PayPal users shot up to 79 million from 50 million a year ago. ebay also earn advertising fees for allow some advertiser posting their advertisement on the website. eBay offers several advertising programs that may help advertisement publishers increase their sales cost-effectively.
eBay Inc. is an American Internet company that manages eBay.com, an online auction and shopping website in which people and businesses buy and sell a broad variety of goods and services worldwide. eBay do not have inventory, it generates revenue from a number of fees. The eBay fee system is quite complex; there are fees to list a product (Insertion Fee) and fees when the product sells (Final Value Fee), plus several optional adornment fees, all based on various factors and scales. eBay may earned transaction fees from each successful transaction made by the bidders or sellers. eBay now owns the Paypal payment system which has fees of its own. Paypal founded in 1998 and acquired by eBay Inc. in October 2002. Paypal enables any individual or business with an email address to securely, easily and quickly send and receive payments online. Paypal's service builds on the existing financial infrastructure of bank accounts and credit cards and uses the world's most advanced proprietary fraud prevention systems to create a safe payment solution. A global leader in online payment solutions, Paypal has tens of millions of registered accounts and is accepted by millions of merchants worldwide, on and off eBay. Revenues from PayPal's transaction fees were $243.9 million, a gain of 51 percent from the year-ago quarter and 145 percent from querter2 2003. And the number of registered PayPal users shot up to 79 million from 50 million a year ago. ebay also earn advertising fees for allow some advertiser posting their advertisement on the website. eBay offers several advertising programs that may help advertisement publishers increase their sales cost-effectively.  Amazon.com, Inc. is an American-based multinational electronic commerce company. Amazon.com is a well known online shopping on the web, it provides a wide range of advertising channels to reach the most demographic availability. Amazon uses the internet as the sole method for selling goods to its consumers. Its major revenue is come from the sales included books, movies, musics, computer, electronic, toys, sports and others on domestic and international Websites, such as Amazon Marketplace. Since year 2000, Amazon.com entered into new partnerships designed to increase the firm's revenue and make it profitable. Example like through its agreement with Greenlight.com, Amazon.com added cars to its product offerings in August 2000. The new link presented information on automobiles and trucks in the standard Amazon.com format.
Amazon.com, Inc. is an American-based multinational electronic commerce company. Amazon.com is a well known online shopping on the web, it provides a wide range of advertising channels to reach the most demographic availability. Amazon uses the internet as the sole method for selling goods to its consumers. Its major revenue is come from the sales included books, movies, musics, computer, electronic, toys, sports and others on domestic and international Websites, such as Amazon Marketplace. Since year 2000, Amazon.com entered into new partnerships designed to increase the firm's revenue and make it profitable. Example like through its agreement with Greenlight.com, Amazon.com added cars to its product offerings in August 2000. The new link presented information on automobiles and trucks in the standard Amazon.com format. Amazon charges a commission rate based on the sales price, a transaction fee, and a variable closing fee for each successful sale. Amazon.com Inc. said that earnings climbed to $177 million, or 41 cents per share, in the first quarter in year 2009 was thanks to strong sales of products.
Related Links:
1. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google
2. http://www.organicspam.com/google_revenue_model.asp
3. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AdWords
4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EBay
5. http://www.ecommerce-guide.com/essentials/ebay/article.php/3522981
6. http://ecommerce.hostip.info/pages/29/Amazon-Com-NEW-PARTNERS-HELP-INCREASE-REVENUE.html
Sunday, June 21, 2009 | Labels: Amazon.com, E-Commerce Revenue Model, eBay, Google | 1 Comments
An Example of an E-Commerce failure and its causes
 Toys "R" Us (currently spelled Toys Я Us in the logo, and before as Toys "Я" Us with a reversal on the "R".) is a toy store chain based in the United States. The chain also has locations in Europe, Asia, Oceania, Africa, and Canada. The company currently operates 585 stores in the United States and 716 stores in 34 other countries, with some of them under franchises or licenses. Being an $11 billion business with 1600 stores worldwide, this huge regime operates in five divisions:
Toys "R" Us (currently spelled Toys Я Us in the logo, and before as Toys "Я" Us with a reversal on the "R".) is a toy store chain based in the United States. The chain also has locations in Europe, Asia, Oceania, Africa, and Canada. The company currently operates 585 stores in the United States and 716 stores in 34 other countries, with some of them under franchises or licenses. Being an $11 billion business with 1600 stores worldwide, this huge regime operates in five divisions:
Toys "R" Us, U.S.

In order to provide the customers the products and services whenever and wherever they need, Toys "R" Us announced its plans to create an e-commerce subsidiary, Toysrus.com. In 1999, Toysrus.com has established as a premier online toy, video game and baby store outlet. Tragedy happened at the end of 1999.
Sunday, June 21, 2009 | Labels: Causes of e-commerce failure, Example of E-Commerce failure, Toys "R" Us | 1 Comments
An example of an E-Commerce success and its causes
 eBay is one of the success example for e-commerce. It is a well known website for everyone. How eBay started? eBay was born over Labor Day weekend in 1995, eBay founder Pierre Omidyar, in an experiment, put a broken laser pointer up for sale online, and to his surprise, found a buyer. When he told the buyer the item was broken, the buyer said: "I' m a collector of broken laser pointers." It was then that Omidyar knew anything was possible. It has around 14 years of history.
eBay is one of the success example for e-commerce. It is a well known website for everyone. How eBay started? eBay was born over Labor Day weekend in 1995, eBay founder Pierre Omidyar, in an experiment, put a broken laser pointer up for sale online, and to his surprise, found a buyer. When he told the buyer the item was broken, the buyer said: "I' m a collector of broken laser pointers." It was then that Omidyar knew anything was possible. It has around 14 years of history.
eBay is The World’s Online Marketplace, enabling trade on a local, national and international basis. With a diverse and passionate community if individuals and small businesses. Besides that, eBay also offers an online platform where millions of items are traded each day. There are about 276 million registered eBay users worldwide until year 2008. More than US$2,039 (RM6,490) worth of goods are traded every second.
Since its initial public offering in 1998, the company has continued to innovate and connect people and not just through its marketplaces. Two critical acquisitions have made eBay Inc. a global leader in online payments (PayPal- acquired in October 2002) and communications (Skype- acquired in October 2005) as well. PayPal enables any individual or business with an email address to securely, easily and quickly send and receive payments online. Acquired by eBay Inc. in October 2002, PayPal builds on the existing financial infrastructure of bank accounts and credit cards and uses the world's most advanced proprietary fraud prevention systems to create a safe payment solution. Today, PayPal is a global leader in online payment solutions: It has 149 million registered users and is accepted by millions of merchants worldwide - on and off eBay. PayPal's Q1 2008 global total payment volume of $14.4 billion accounted for nearly 9 percent of worldwide eCommerce.
PayPal enables any individual or business with an email address to securely, easily and quickly send and receive payments online. Acquired by eBay Inc. in October 2002, PayPal builds on the existing financial infrastructure of bank accounts and credit cards and uses the world's most advanced proprietary fraud prevention systems to create a safe payment solution. Today, PayPal is a global leader in online payment solutions: It has 149 million registered users and is accepted by millions of merchants worldwide - on and off eBay. PayPal's Q1 2008 global total payment volume of $14.4 billion accounted for nearly 9 percent of worldwide eCommerce.
Acquired by eBay Inc. in October 2005, Skype is an Internet communication company that has revolutionized the way people talk online. With more than 309 million registered users as of early 2008, Skype allows people everywhere to make unlimited voice and video calls online for free using its software. Skype is available in 28 languages and is used in almost every country on Earth. This business unit generates revenue through its premium offerings, such as calls (using its software) made to and from landline and mobile phones; voicemail; call forwarding; and personalization, including ringtones and avatars. In addition to its presence on eBay, Skype has relationships with a growing network of hardware and software providers.
Other key acquisitions have strengthened eBay Inc.'s portfolio of ecommerce companies, including shopping.com, a pioneer in online comparison shopping; Stubhub, a leading online marketplace for the resale of event tickets; rent.com, the most visited online apartment listing service in the U.S.; StumbleUpon, an online solution that helps people discover and share content on the web; and market-leading online classifieds sites including LoQUo.com, Intoko, and Netherlands-based Marktplaats.nl. The company has also grown its classifieds business through Kijiji, which launched in the U.S. in 2007.
Causes of its success:
(a) eBay's success is based on its ability to transform many fragmented, primarily local markets into global ones at a relatively low cost to its users. People have always had a need and an interest in buying and selling used, surplus, and collectible items. Traditionally, they have done so through garage sales, classified advertising in local newspapers, and flea markets.
(b) For a price comparable to advertising an item in the classifieds section of their local newspaper with three or four lines of text, users can post lengthy descriptions and pictures available to a worldwide audience. Concerns about fraud have been mitigated through a user feedback system escrow services. The company's ability to bring a large number of buyers and sellers together is what has driven its growth. The more buyers there are, the more sellers want to participate. Conversely, the more sellers there are, the more items are to buy, and the greater the attraction of the service to buyers. eBay has allowed many people to become entrepreneurs with little upfront expense or overhead and provides a method for companies and even governments to dispose of unwanted items.
(c) eBay makes money by charging listing fees and collecting a percentage of the selling price of items sold through the site. eBay also owns PayPal, which makes money through investing its clients' assets and from transaction fees. eBay's growth has been remarkable.
(d) eBay appears to have significant growth potential. It has successfully introduced new markets, such as car sales, which many thought would not be adaptable to its business model. Besides that, it is so successful because it meets its customer's needs better than any competing service. No one else has accumulated such a large number of buyers and sellers in a single marketplace.
(e) According to the interview with the spokesperson of eBay, Kevin Pursglove, he thinks that people really enjoy the experience of the shopping bazaar. They enjoy the hunt. They enjoy looking around for merchandise.
(f) The other component is that Kevin Pursglove believes they really enjoy the competition of the bidding process. Everybody likes to get a bargain, and everybody, I think, in some way, shape, or form, likes to haggle a little bit over the price. Their auction format allows users to do that.
Video Clips:
1)Brief introduction of eBay
2) eBay music video (Have fun XD)
Related Links:
1. http://www.ebay.com/
2. http://www.ecommercetimes.com/story/2127.html?welcome=1213184390
3. http://answers.google.com/answers/threadview?id=245309
4. http://www.neowave.com.my/malaysia_ecommerce_radar.asp
5. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pt0qIPAeLXM - source from WatchMojo
6. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3YXHcbX36Ao - source from dps001
Sunday, June 21, 2009 | Labels: Causes of e-ccommerce success, eBay, Example of E-Commerce success, PayPal, Skype | 2 Comments
- 3rd party certification
- Advantages of E-Commerce
- AirAsia
- Amazon.com
- Causes of credit card debts
- Causes of e-ccommerce success
- Causes of e-commerce failure
- Corporate Blogging
- Credit card debts
- Customer's adoption strategies
- Dell
- Digicert Sdn Bhd
- Disadvantages of E-Commerce
- E-Auction
- E-Commerce Revenue Model
- E-currency
- E-gold
- E-learning
- E-money
- eBay
- Electronic learning
- Electronic payment
- Evolution of E-Commerce
- Example of E-Commerce failure
- Example of E-Commerce success
- Example of phishing
- History of E-Commerce
- Locat transactional e-commerce site
- MEPS cash
- Mobile payment systems
- Msctrustage.com
- Online security
- PayPal
- Phishing
- Phishing prevention methods
- Potentials of mobile payment system
- Pre-paid cash card
- Prevention of credit card debts
- Safeguard financial data
- Safeguard personal data
- Self-introduction
- Skype
- Touch N Go
- Toys "R" Us
Blog Archive
-
▼
2009
(24)
-
▼
June
(14)
- Buy Air Asia merchandise online
- The application of 3rd party certification program...
- How to safeguard our personal and financial data?
- Phishing: Examples and its prevention methods
- The threat of online security: How safe is our data?
- Advantages and disadvantages of E-Commerce
- Revenue Model for Google, eBay & Amazon.com
- An Example of an E-Commerce failure and its causes
- An example of an E-Commerce success and its causes
- The history and evolution of E-Commerce
- About - Mei Yee -
- About - Seok Fen -
- About - Hui Jing -
- About - Pei Yee -
-
▼
June
(14)
- E-Commerce Land
- Fortune 500 Business Blogging Wiki
- Malaysia E-Commerce News
- The New PR/Wiki - Corporate Blogs List
- Wikipedia - About Corporate Blogging
- Wikipedia - About E-Commerce
- Wikipedia - About E-Currency
- Wikipedia - About E-Learning
- Wikipedia - About eBay
- Wikipedia - About Google
- Wikipedia - About Toys "R" Us